REITs – Meaning
Real estate as an investment option is mostly unaffordable for most Indian retail investors. The Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) announced in the Union Budget 2014–15 enable investors to collectively invest in commercial properties and earn a profit from such investments. At the same time, REITs provide an alternative funding channel for the realty sector.
In India, REITs were first formally introduced by the Securities & Exchange Board (SEBI) in 2007 as draft REIT Regulations. However, due to structural limitations in the draft regulations, they were never finalized & announced. In September 2013, SEBI released a revised set of draft REIT Regulations.
REITs are expected to provide low and mid-income investors with the opportunity of becoming stakeholders in a portfolio of real estate assets, which would otherwise have not been feasible.
Simply put – It’s a Real Estate Mutual Fund
REITs are investment trusts that work similar to mutual funds with the only big difference being that Instead of using the money collected from investors to buy stocks and bonds, REITs invest in commercial properties generating rental income. It’s like a pooling vehicle through which capital is deployed to own real estate assets. REITs will be listed on recognized stock exchanges and will be freely tradeable.
REITs – Guidelines
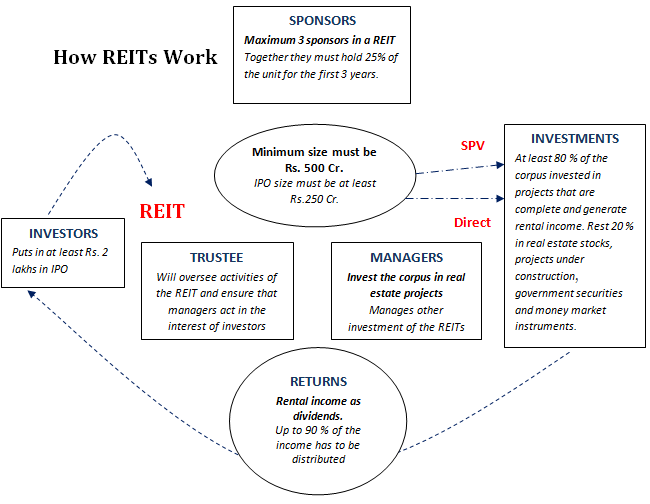
- The REIT shall be set up as a Trust under the provisions of the Indian Trusts Act, 1882 and will have a trustee, 3 sponsors (holding at least 25% of the units), manager, and a principal valuer.
- The trustee will be registered with SEBI.
- REIT will raise funds through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). The minimum issue size of the offer has been specified at Rs. 250 Cr. and the size of assets under the REITs should not be less than Rs 500 Cr.
- The minimum subscription size (in IPO) for units of REIT is currently set at Rs. 2 lakh.
- Trading lot for such units shall be Rs.1 lakh.
- It will be mandatory to make continuous disclosures in accordance with clause 49 of the listing agreement.
- REITs will only be allowed to invest in commercial real estate, either directly or through SPVs.
- An REIT shall invest in at least 2 projects with not more than 60 % of the total investment in a single project.
- In addition, at least 80 % of a REIT’s assets must be revenue-generating properties and not more than 20 %of the value of REIT assets shall be invested in developmental properties and mortgage backed securities, real estate stocks, government securities and money market instruments.
- REITs must distribute at least 90 % of their net distributable cash flows to their investors every six months as dividends.
- REITs must mandatorily do full valuation on an annual basis and must provide an update of valuation on half yearly basis.
- The net asset value (NAV) must be disclosed within 15 days from the date of such valuation/updation.
Benefits of investing in REITs
- Low cost property ownership – Provides investor an ability to participate in real estate ownership with a low investment amount of Rs. 2 lakhs which means that investors can diversify their portfolios by including real estate without investing a huge amount in the real estate market. Also, investors will benefit from real estate price appreciation without any difficulty associated with buying and maintaining a property.
- Liquidity: Compared to investing directly in the real estate market, REIT investors benefit from greater liquidity as REITs are traded on the stock exchanges just like any other equity shares and mutual funds.
- Diversification: Investors can gain from the large and diversified corpus of a REIT as opposed to having a single asset exposure. Investing in a range of properties helps an investor minimize risk and participate in a wide range of investment opportunities.
- Regular dividends: REITs are mandated to distribute at least 90 % of their distributable cash flows as dividend on a half yearly basis. This ensures continuous stream of revenue to the investors in addition to appreciation in the underlying value of REIT assets, and consequently the trading price of the REIT units.
- Transparency. Often, it is difficult for retail investors to get complete information about a property. With a professionally managed trust, investors can rely on their disclosure standards as REITs are required to make regular disclosures, including quarterly and yearly financial reports.
The introduction of REITs in India will not only provide a new source of cash to developers who have struggled to reduce their debt burden but will also give investors the ability to diversify their portfolios by owning real estate assets.


Thanks for REIT information,can you provide more detail about REIT with How to do Legal Formalities and Paper work,Licence Etc, and What is Provision for REIT in the Indian Income Tax Department. Once again Thank you very much.
Sure. I will try to write on this soon.
Are there any REITs we can already invest in right now?
Thanks for a sharing the informative of REIT. It is helpful to us for government working area of real estate sector. Thank for you once again.
Really interested to startup an REIT Fund.
Still doing my homework – your article helped.
Would be great if you could share some more info over an email.
What exactly do you want to know. Email me!